#P15157. [SWERC 2024] Disk Covering
[SWERC 2024] Disk Covering
题目描述
:::align{center}
 :::
:::
On a vast, flat green meadow, there are several golden disks in the shape of perfect circles from ancient times. According to legend, if one chants a spell, the area covered by the disks will turn into flames, fending off enemy attacks. When the enemy comes, you can hide in a place completely surrounded by disks, yet not on the disks, thus isolated from the outside world by the flames.
Given the positions and sizes of the disks, determine whether such a hiding place exists.
输入格式
The first line contains an integer , representing the number of disks. In the following lines, the line contains three integers that describe disk : the x-coordinate , the y-coordinate of its center, and its radius .
输出格式
A single integer, if such a place exists, or otherwise.
4
-6 0 8
-4 10 7
4 4 6
8 14 2
0
5
4 -2 5
-4 -2 5
-8 8 8
4 6 5
-6 4 2
1
3
420 580 230
200 200 200
600 200 210
0
提示
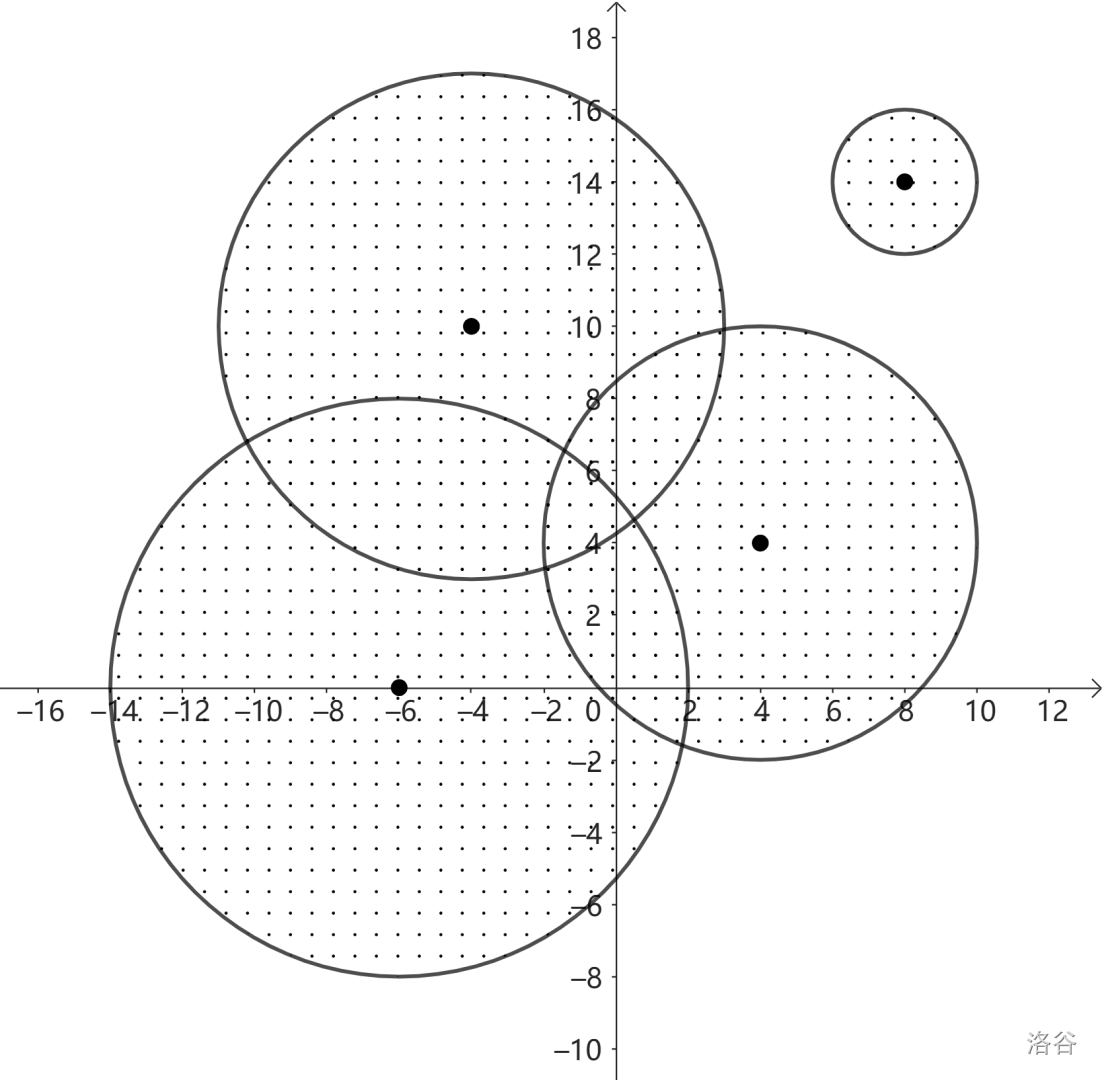
Sample Explanation 1
In this sample, there isn’t any place that is completely surrounded by disks, yet not on the disks.
:::align{center}
 :::
:::
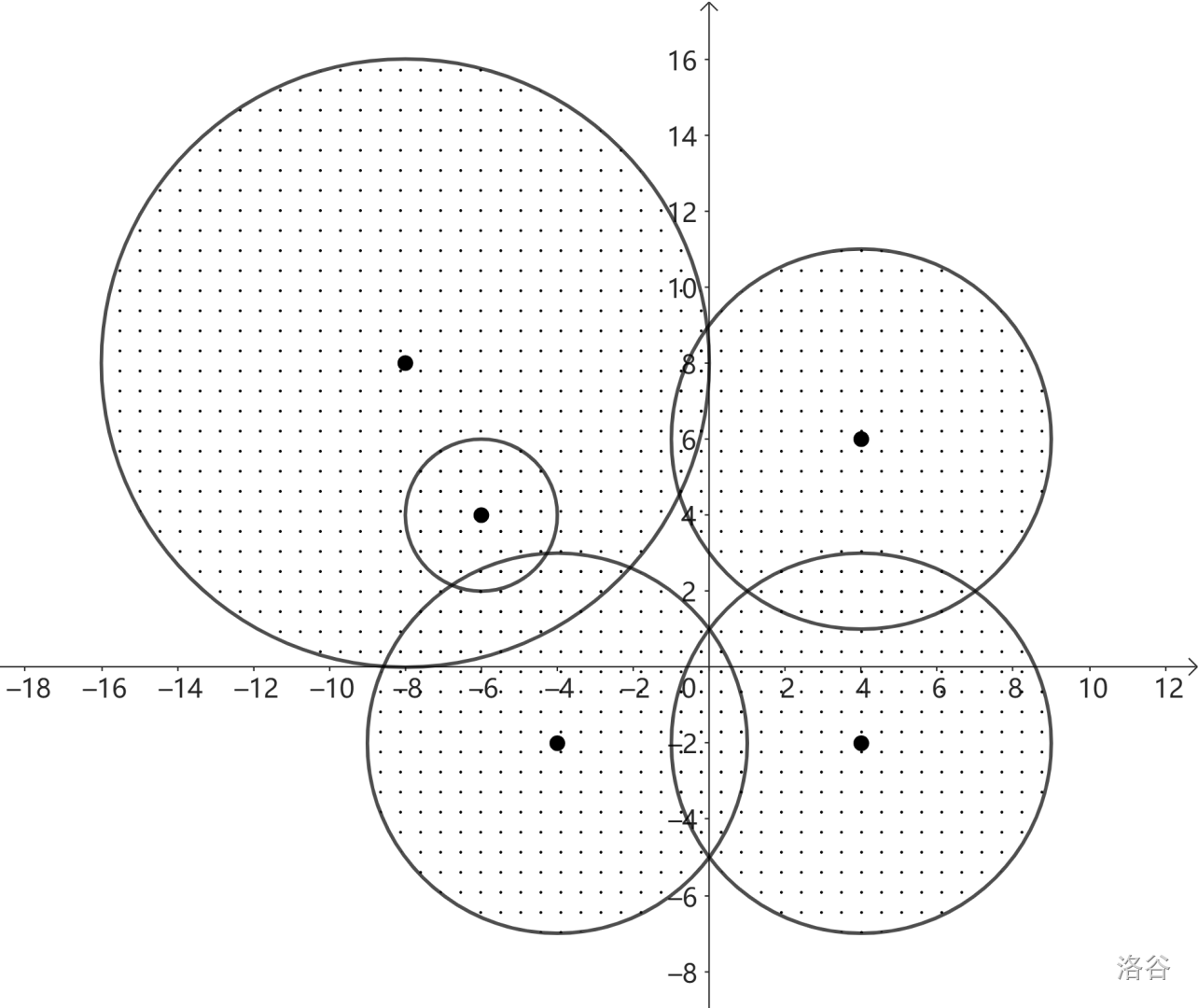
Sample Explanation 2
In this sample, is one of the places we can hide. It is surrounded by disks, yet not on the disks. Note that although all the inputs are integers, the hiding place does not necessarily have to be an integer point.
:::align{center}
 :::
:::
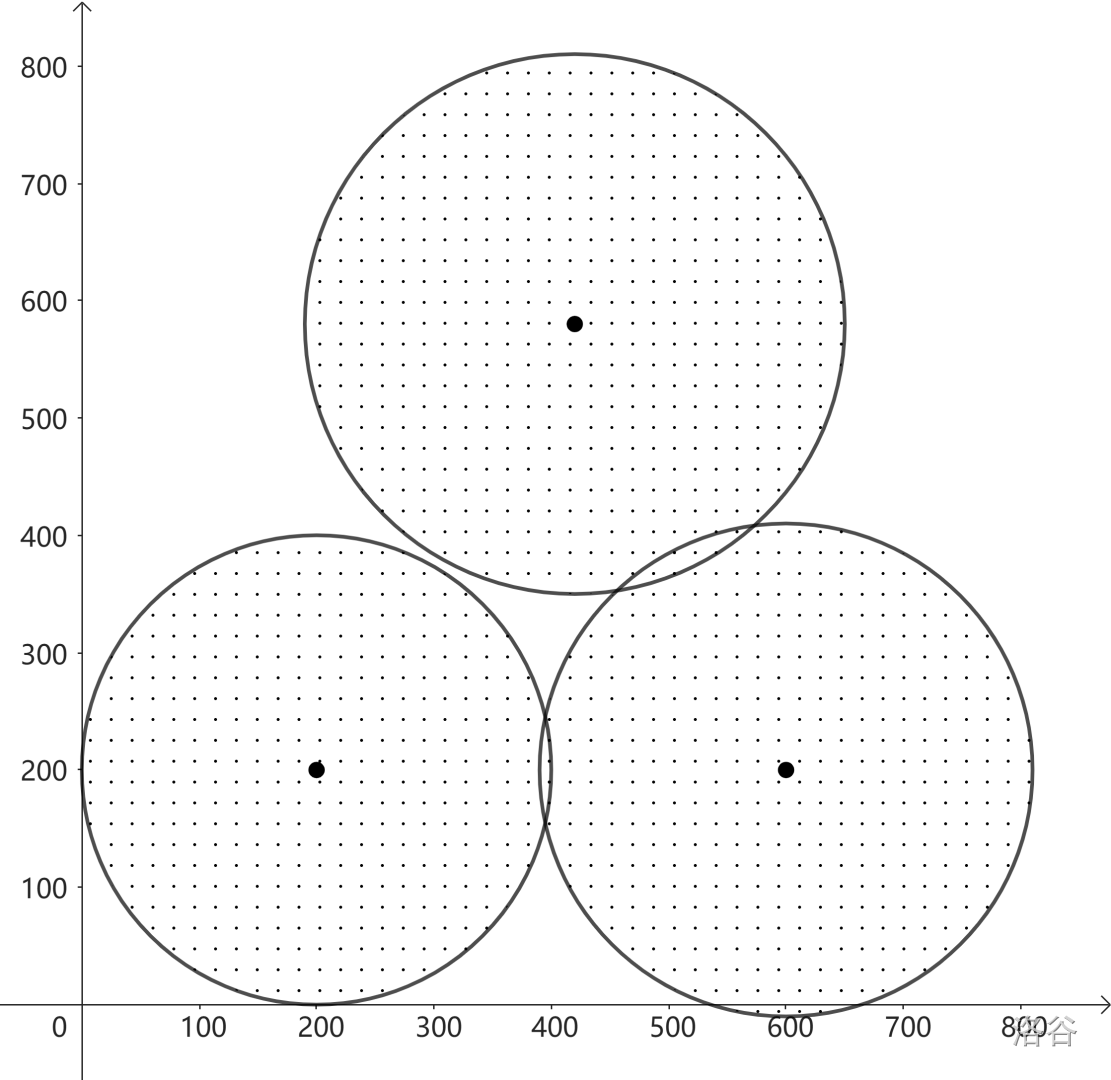
Sample Explanation 3
In this sample, there isn’t any place that is completely surrounded by disks, yet not on the disks.
:::align{center}
 :::
:::
Limits
- ;
- for all ;
- for all ;
- There are no three disks whose circular outlines intersect at a common point;
- Among all intersection points of the circular outlines of any two disks, the distance between any two intersection points is greater than or equal to ;
- There are no two disks whose circular outlines are tangent to each other (i.e. have exactly one intersection point);
- For two disks whose circular outlines do not intersect, the distance between any point on the circular outline of one disk and any point on the circular outline of the other disk is always greater than or equal to .
