#P15084. [ICPC 2024 Chengdu R] Two Convex Holes
[ICPC 2024 Chengdu R] Two Convex Holes
题目描述
Consider two opaque planes and () in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. Each plane has a convex polygonal hole, denoted as and respectively, which allows light to pass through.
There is a point light source moving in the plane (), in a direction parallel to the plane. The light source starts at the initial position at time and moves with a constant velocity . Therefore, at any time , the position of the light source is given by .
For a point in the plane , define it as at time if and only if the segment intersects the interiors (including boundaries) of both polygons and . The at time , denoted as , is the area formed by all illuminated points in the plane .
Define the over the time period , denoted as , as the expected value of over the interval , assuming is a uniformly distributed random variable over .
Given multiple time periods , your task is to find the average illuminated area for each of these periods.
输入格式
The first line contains a single integer () indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains five integers , , , , (, , ), representing the initial position of the light source and its velocity vector . It is guaranteed that .
The second line contains two integers and (, ), indicating the number of vertices of polygon and the value of . Each of the following lines contains two integers and (), describing the vertices of in counterclockwise order.
The following line contains two integers and (, ), indicating the number of vertices of polygon and the value of . Each of the following lines contains two integers and (), describing the vertices of polygon in counterclockwise order.
It is guaranteed that no three or more vertices are collinear for and .
The following line contains an integer (), indicating the number of queries. Each of the following lines contains two integers and (), representing a time period.
It is guaranteed that the sum of and the sum of over all test cases do not exceed , respectively, and .
输出格式
For each query, output a real number representing the average illuminated area. Your answer will be considered correct only if the relative or absolute error between your answer and the correct answer does not exceed .
1
0 0 3 0 -1
4 1
1 0
3 0
3 2
1 2
4 2
0 0
1 0
1 1
0 1
3
0 10
1 2
1 1
0.450000000
1.125000000
2.250000000
提示
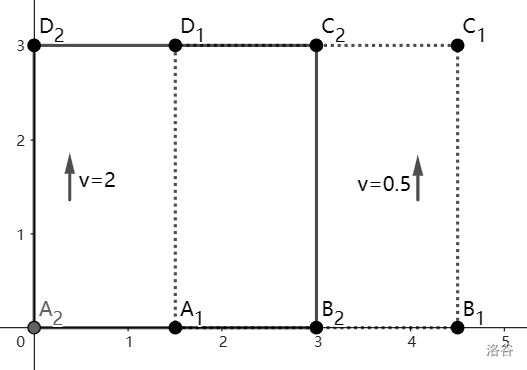
For the example, the projections of convex polygons and onto the plane at , and the movement of these projections, are illustrated below. Polygon is the projection of polygon , and polygon is the projection of polygon .
:::align{center}
 :::
:::
